The Role of Physical Therapy in Postpartum Recovery
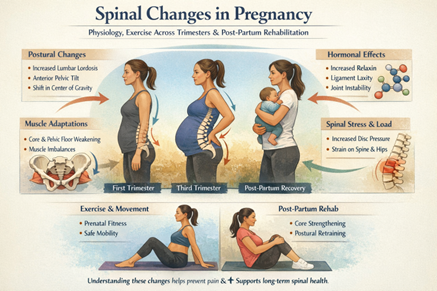
Postpartum recovery is a crucial phase that involves healing and restoring the body after childbirth. Physical therapy plays a vital role in helping new mothers regain strength, mobility, and function during this period. Here are the key ways physical therapy supports postpartum recovery:
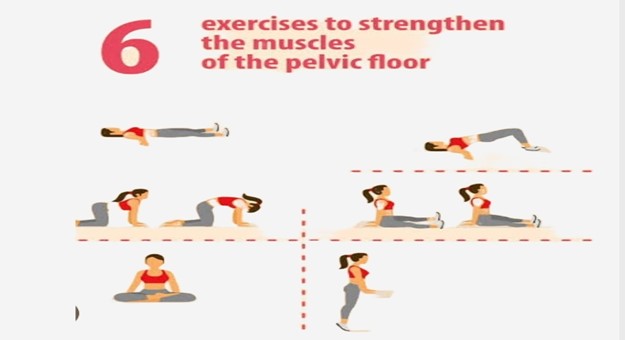
1. Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation:
Childbirth, whether vaginal or via cesarean delivery, can strain or damage the pelvic floor muscles. Physical therapy helps in:
- Assessing pelvic floor strength and function.
- Treating conditions like urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and pain during intercourse.
- Teaching pelvic floor exercises such as Kegels to improve muscle tone and support core stability.
2. Core Strengthening:
The abdominal muscles, particularly the rectus abdominis, may separate during pregnancy, a condition known as diastasis recti. Physical therapists assist by:
- Designing safe, targeted exercises to close the abdominal gap.
- Avoiding activities that exacerbate the separation.
- Rebuilding core stability, which is essential for posture and back support.
3. Posture and Alignment Correction:
Postpartum posture often suffers due to the physical demands of caring for a newborn, such as breastfeeding, lifting, and carrying. Physical therapy focuses on:
- Correcting posture to prevent back, neck pain, and shoulder pain.
- Teaching ergonomic techniques for daily activities.
- Strengthening muscles that support proper alignment.
4. Managing Pain and Discomfort:
Pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis is common after delivery. Physical therapists use techniques such as:
- Manual therapy to reduce muscle tension and improve mobility.
- Taping or bracing for additional support during recovery.
- Modalities like heat, cold therapy, or electrical stimulation for pain relief.
5. C-Section Recovery:
For mothers who undergo a cesarean delivery, physical therapy can aid in:
- Managing scar tissue through gentle mobilization.
- Reducing pain and tightness around the incision area.
- Gradually reintroducing physical activity and strengthening the abdominal wall.
6. Mental Health Support:
Physical therapy indirectly contributes to mental health by:
- Promoting physical activity, which releases endorphins and reduces stress.
- Addressing body image concerns by helping mothers feel stronger and more in control of their bodies.
- Encouraging relaxation through breathing exercises and gentle stretches.
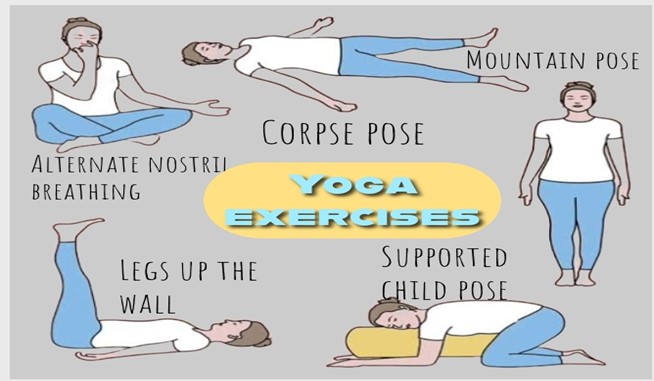
7. Safe Return to Exercise:
Physical therapists guide new mothers in safely resuming physical activity by:
- Evaluating readiness based on individual recovery.
- Recommending low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga.
- Gradually progressing toward higher-intensity workouts without risking injury.
Conclusion:
Physical therapy is an invaluable component of postpartum recovery. By addressing the physical challenges that arise after childbirth, physical therapists empower women to heal, regain confidence, and return to their daily activities with improved function and comfort. A personalized approach ensures that each mother receives care tailored to her unique needs, promoting a smoother and healthier recovery journey.