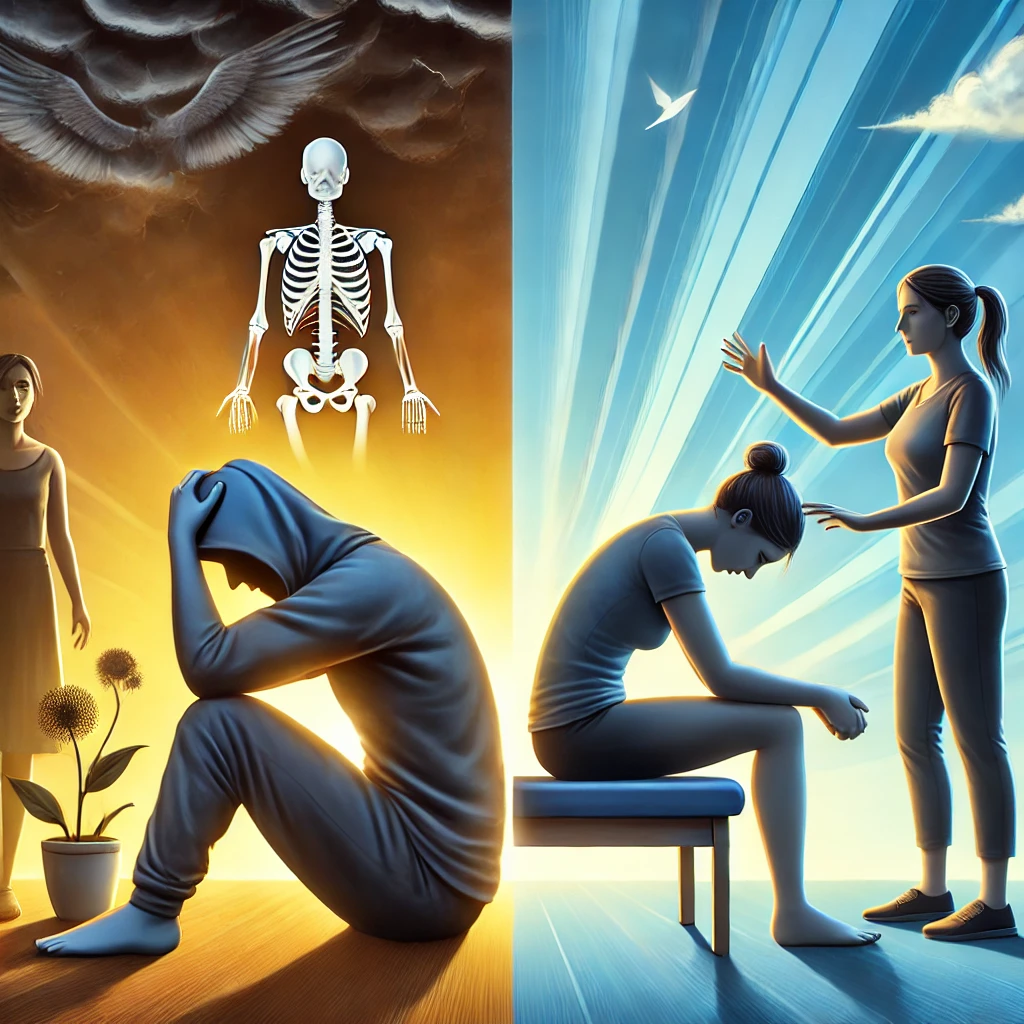
Anxiety and depression are among the most prevalent mental health conditions worldwide, often leading to significant physical and psychological distress. While traditional treatments such as psychotherapy and medication are widely used, physical therapy in anxiety and depression has emerged as a complementary approach that enhances mental well-being through movement, relaxation techniques, and structured physical activity.
Physical Therapy in Anxiety and Depression
-
Enhancing Mood Through Physical Activity:
Physical activity is known to stimulate the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Additionally, exercise increases the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, both of which are associated with emotional stability and happiness. Engaging in structured physical therapy can:
– Reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by promoting neurochemical balance.
– Enhance self-confidence and overall mental well-being.
– Improve energy levels and reduce fatigue, which is common in individuals with depression.
-
Alleviating Physical Symptoms Associated with Anxiety and Depression:
Many individuals experiencing anxiety and depression report physical symptoms such as muscle tension, headaches, chronic pain, and fatigue. Physical therapy addresses these issues through:
– Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Helps release muscle tension and improves posture, reducing physical discomfort.
– Massage Therapy: Alleviates stress-related muscle tightness and promotes relaxation.
– Pain Management Techniques: Guides individuals in managing chronic pain that may contribute to depressive symptoms.
-
Relaxation and Breathing Techniques for Stress Reduction:
Physical therapists incorporate breathing exercises and relaxation techniques to help individuals regulate their stress response. Some common techniques include:
– Diaphragmatic Breathing: Encourages deep breathing, reducing hyperventilation and panic symptoms.
– Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): A systematic approach to relieving tension throughout the body.
– Mindfulness and Meditation Practices: Helps individuals stay present and reduce overwhelming thoughts.
-
Improving Sleep Quality:
Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or restless sleep, are common in individuals with anxiety and depression. Engaging in regular physical activity under the guidance of a physical therapist can:
– Regulate sleep patterns by reducing stress hormones like cortisol.
– Enhance deep sleep stages, promoting better rest and recovery.
– Address physical discomfort that may contribute to sleep disruptions.
-
Encouraging Routine and Behavioral Activation:
One of the challenges in managing depression is the lack of motivation to engage in daily activities. Physical therapy helps establish a structured routine, providing individuals with:
– A sense of accomplishment through small, achievable physical goals.
– Increased motivation by gradually engaging in physical movement.
– A distraction from negative thought patterns and rumination.
-
Social Interaction and Emotional Support:
Physical therapy often involves guided sessions with a professional, providing a supportive environment for individuals struggling with isolation. Additionally, group therapy exercises and community fitness programs encourage social interaction, which can be beneficial in reducing feelings of loneliness and withdrawal.
-
Addressing Chronic Pain and Physical Health Conditions:
Chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, and lower back pain, are commonly linked with depression. A physical therapist designs personalized treatment plans to:
– Strengthen muscles and joints to reduce discomfort.
– Teach pain management strategies that improve mobility and function.
– Improve overall physical health, indirectly boosting mental well-being.
Conclusion:
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing anxiety and depression by integrating movement, relaxation techniques, and structured physical routines. While it does not replace psychological interventions, physical therapy in anxiety and depression serves as a valuable complementary approach that enhances both physical and emotional health. By addressing the interconnected relationship between the body and mind, physical therapy in anxiety and depression empowers individuals to regain control over their well-being and improve their quality of life.
About Authors
Dr. Muhammad Mahmood Ahmad is a Spinal as well as an Orthopedic Surgeon with over 14 years of experience currently practicing at Razia Saeed Hospital, Multan.