Low back pain (LBP) is a common health concern among office workers due to prolonged sitting, poor posture, and inadequate ergonomic practices. It affects productivity, quality of life, and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and management strategies can help reduce the prevalence of LBP in office settings.
Causes of Low Back Pain in Office Workers:
1) Prolonged Sitting:
– Extended sitting increases pressure on the spine, leading to muscle stiffness and reduced blood circulation.
– Lack of movement weakens the core muscles, making the lower back more vulnerable to strain.
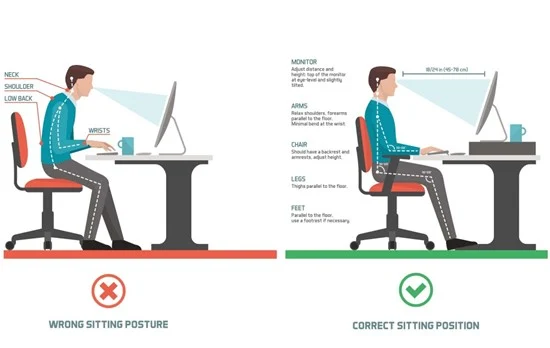
2) Poor Posture:
– Slouching, leaning forward, or sitting without back support can cause spinal misalignment and muscle imbalances.
– Improper workstation setup, such as a low chair height or an incorrectly positioned computer screen, contributes to poor posture.
3) Lack of Physical Activity:
– Sedentary lifestyles lead to weak core and back muscles, reducing spinal support and increasing the risk of pain.
– Limited stretching and mobility exercises contribute to muscle tightness and stiffness.
4) Inadequate Ergonomics:
– Poorly designed office chairs, desks, and workstations force workers into uncomfortable postures, leading to chronic back pain.
– Incorrect monitor height and keyboard positioning strain the neck and lower back.
5) Psychological Stress:
– Workplace stress and anxiety can cause muscle tension, exacerbating back pain.
– Mental health factors, such as job dissatisfaction and high workload, may increase the perception of pain.
6) Lifestyle Factors
a) Work-Life Balance:
– Long Working hours
– Insufficient sleep
– Lack of leisure activities
– Conflicting work and family responsibilities
b) Dietary Insufficiency:
– Poor nutrition
– Inadequate hydration
– Lack of essential vitamins and minerals (e.g vitamin D, calcium)
– Excessive caffeine or sugar consumption
Prevention and Management of Low Back Pain
1) Ergonomic Adjustments:
Chair Selection: Use an adjustable chair with lumbar support, ensuring the backrest supports the natural curve of the spine.
Desk and Monitor Positioning: Keep the monitor at eye level and arm’s length away to avoid straining the neck and back.
Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Position them close to the body to minimize unnecessary reaching and wrist strain.
2) Maintaining Proper Posture:
– Keep feet flat on the floor and knees at a 90-degree angle.
– Sit with the back straight, shoulders relaxed, and elbows close to the body.
– Avoid crossing legs, which can lead to spinal misalignment.
3) Incorporating Movement and Exercise:
– Take short breaks every 30–60 minutes to stand, stretch, or walk.
– Perform simple exercises, such as pelvic tilts, seated spinal twists, and hamstring stretches.
– Engage in core-strengthening exercises, such as planks and bridges, to support spinal stability.
4) Stress Management:
– Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce muscle tension.
– Maintain a work-life balance to minimize stress-related pain.
5) Seeking Medical Help:
– If pain persists for more than a few weeks, consult a healthcare professional for assessment and treatment.
– Physical therapy, chiropractic care, or pain management strategies may be recommended for chronic cases.
Conclusion:
Low back pain among office workers is a significant issue that can be prevented and managed through proper ergonomics, posture correction, regular movement, and stress management. Employers and employees should work together to create a healthy workplace that promotes spinal health and reduces the risk of chronic pain.
About Authors
Dr. Muhammad Mahmood Ahmad is a Spinal as well as an Orthopedic Surgeon with over 14 years of experience currently practicing at Razia Saeed Hospital, Multan.