Ultrasound therapy is a popular modality in physical therapy that harnesses the power of high-frequency sound waves to promote healing, reduce pain and inflammation, and improve tissue repair. In this article, we’ll explore the effects, uses, and mechanism of action of ultrasound therapy in physical therapy, as well as its benefits and potential limitations.
How Ultrasound Therapy Works
Ultrasound therapy works by generating high-frequency sound waves that penetrate deep into tissues, promoting healing and relaxation. The therapy can be used to treat a range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, arthritis, and fibromyalgia.
Effects of Ultrasound Therapy
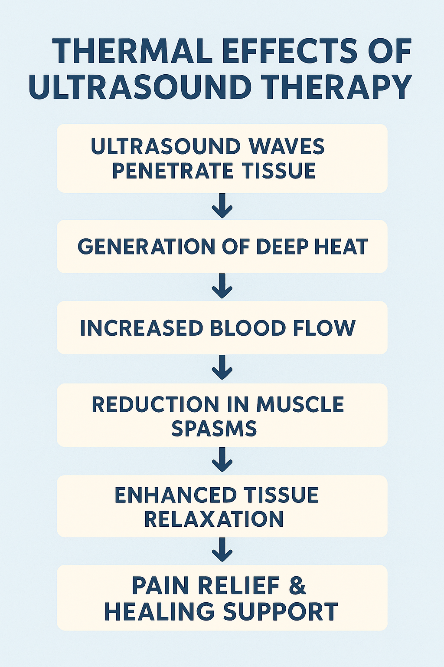
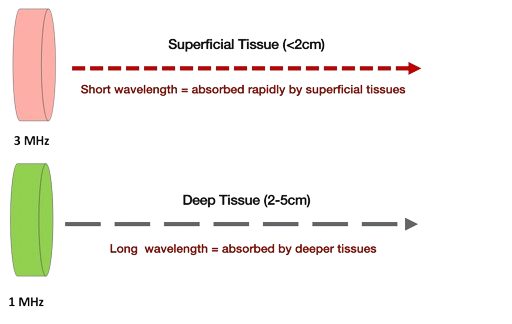
1. Thermal Effects: Ultrasound therapy generates heat within tissues, increasing blood flow, reducing muscle spasms, and promoting relaxation.
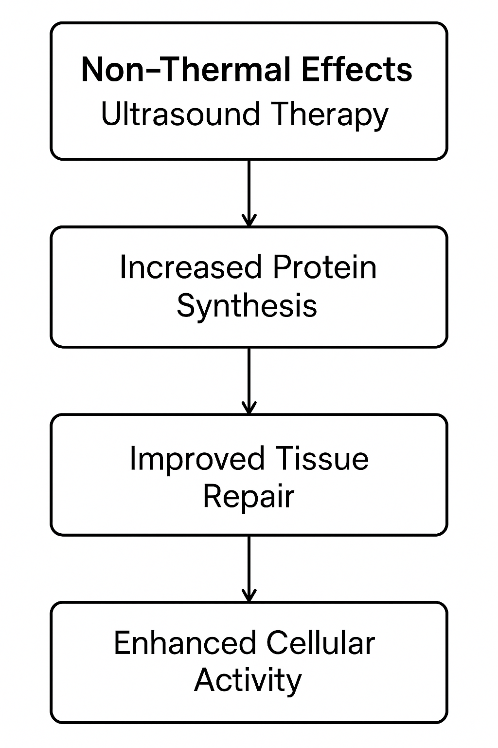
2. Non-Thermal Effects: Ultrasound therapy also produces non-thermal effects, including increased protein synthesis, improved tissue repair, and enhanced cellular activity.
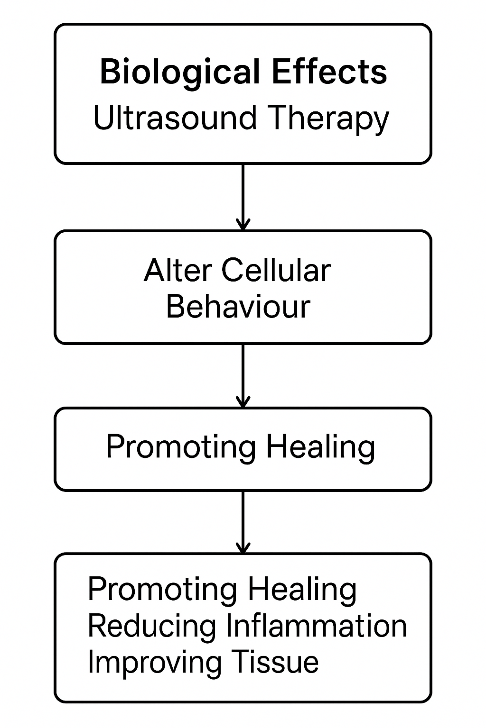
3. Biological Effects: Ultrasound therapy can alter cellular behaviour, promoting healing, reducing inflammation, and improving tissue regeneration.
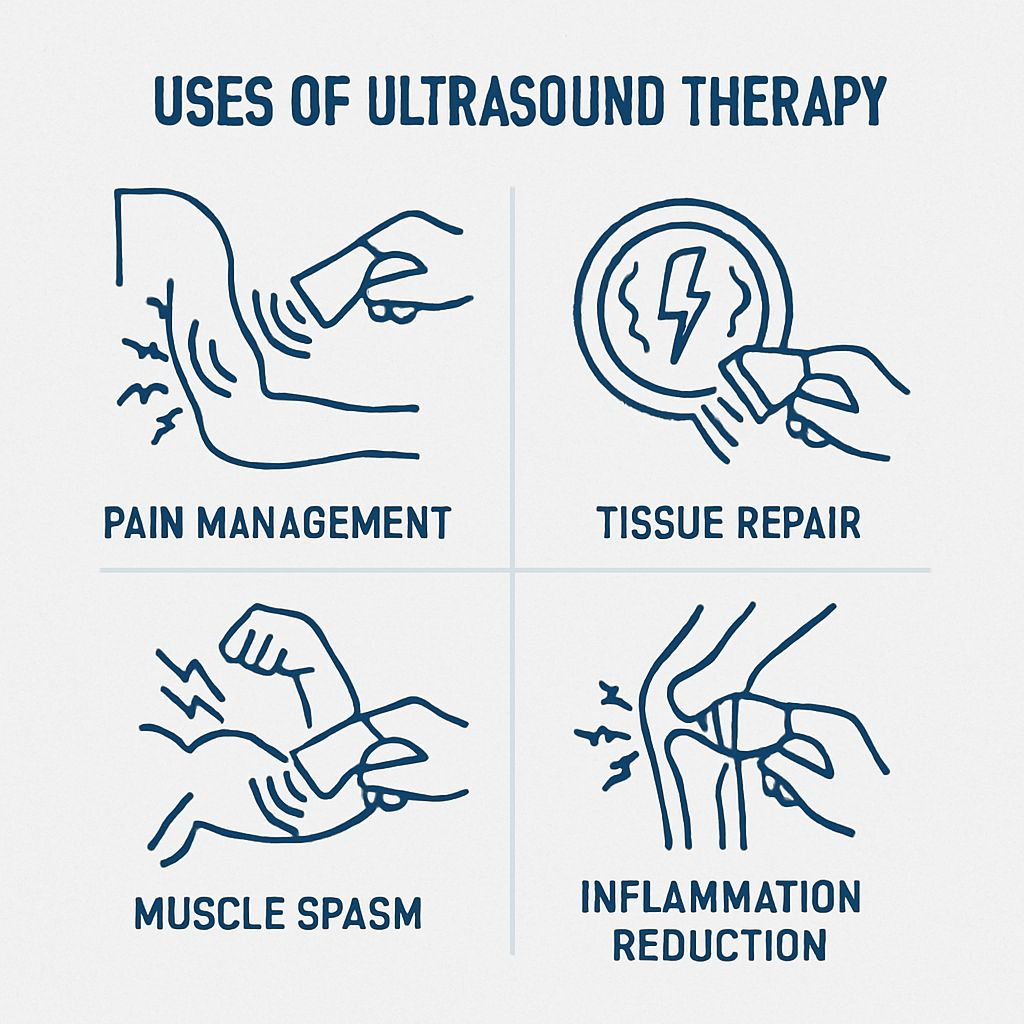
Uses of Ultrasound Therapy
- Pain Management: Ultrasound therapy is used to manage chronic and acute pain, including pain associated with musculoskeletal injuries, arthritis, and fibromyalgia.
- Tissue Repair: Ultrasound therapy promotes tissue repair and regeneration, making it an effective treatment for wounds, tendonitis, and ligament sprains.
- Muscle Spasms: Ultrasound therapy can reduce muscle spasms and promote relaxation, making it beneficial for patients with musculoskeletal injuries.
- Inflammation Reduction: Ultrasound therapy can reduce inflammation, making it an effective treatment for conditions such as tendinitis and bursitis.
Common Conditions Treated with Ultrasound Therapy
- Musculoskeletal injuries: Sprains, strains, and tears
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons
- Bursitis: Inflammation of bursae
- Arthritis: Joint pain and inflammation
- Fibromyalgia: Chronic pain and fatigue
- Wound healing: Promoting tissue repair and regeneration
- Post-operative rehabilitation: Reducing pain and inflammation after surgery
When to Avoid Ultrasound Therapy
While ultrasound therapy is generally safe, there are some situations where it may not be suitable. These include:
- Pregnancy: Ultrasound therapy should be avoided during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester.
- Cancer: Ultrasound therapy may not be suitable for patients with cancer, especially if the cancer is in the treatment area.
- Pacemakers: Ultrasound therapy may interfere with pacemakers and other implanted medical devices.
- Open wounds: Ultrasound therapy may not be suitable for open wounds or skin infections.
- Fractures: Ultrasound therapy may not be suitable for fractures, especially if the fracture is not stable.
Treatment Parameters
- Frequency: 1-3 MHz
- Intensity: 0.5-2.0 W/cm²
- Duration: 5-10 minutes per treatment session
- Mode: Continuous or pulsed
Conclusion:
Ultrasound therapy is a valuable modality in physical therapy, offering a range of benefits for patients with musculoskeletal injuries and conditions. Its thermal, non-thermal, and biological effects make it an effective treatment for pain management, tissue repair, and inflammation reduction. While it’s generally safe, there are some situations where ultrasound therapy may not be suitable. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and optimal treatment parameters for ultrasound therapy.
About Authors
Dr. Muhammad Mahmood Ahmad is a Spinal as well as an Orthopedic Surgeon with over 14 years of experience currently practicing at Razia Saeed Hospital, Multan.